Address
312-F E. Market St.
Leesburg, VA 20176
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 5PM
Regulatory agencies increasingly recognize that traditional animal models often fail to predict human responses in drug safety assessment. To improve human relevance, the FDA is investing heavily in:
These models are emerging as New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) and potential sources of mechanistic real-world evidence, particularly useful where clinical data is limited or human trials are risky.
Cognizance scientific teams played a major role in generating reproducible MPS data, validating system performance, and providing interpretive frameworks for regulatory use.
Despite their promise, Microphysiological Systems face several adoption barriers:
1. Lack of standardized testing workflows – Different labs operate MPS devices differently, producing variable outputs.
2. Difficulty comparing MPS outputs across platforms – No single “reference standard” exists for many endpoints.
3. Limited understanding of translational validity – Regulators need to know if an MPS model predicts human physiology reliably.
4. Need for scalable readouts – To be regulatory-useful, assays must work with reproducible biomarkers, analytics, or AI-enabled interpretation.
5. Data complexity – MPS outputs are multidimensional (electrical, biochemical, morphological) and require sophisticated analytics.
These gaps limited regulatory acceptance – until systematic validation and benchmarking work began to address them.
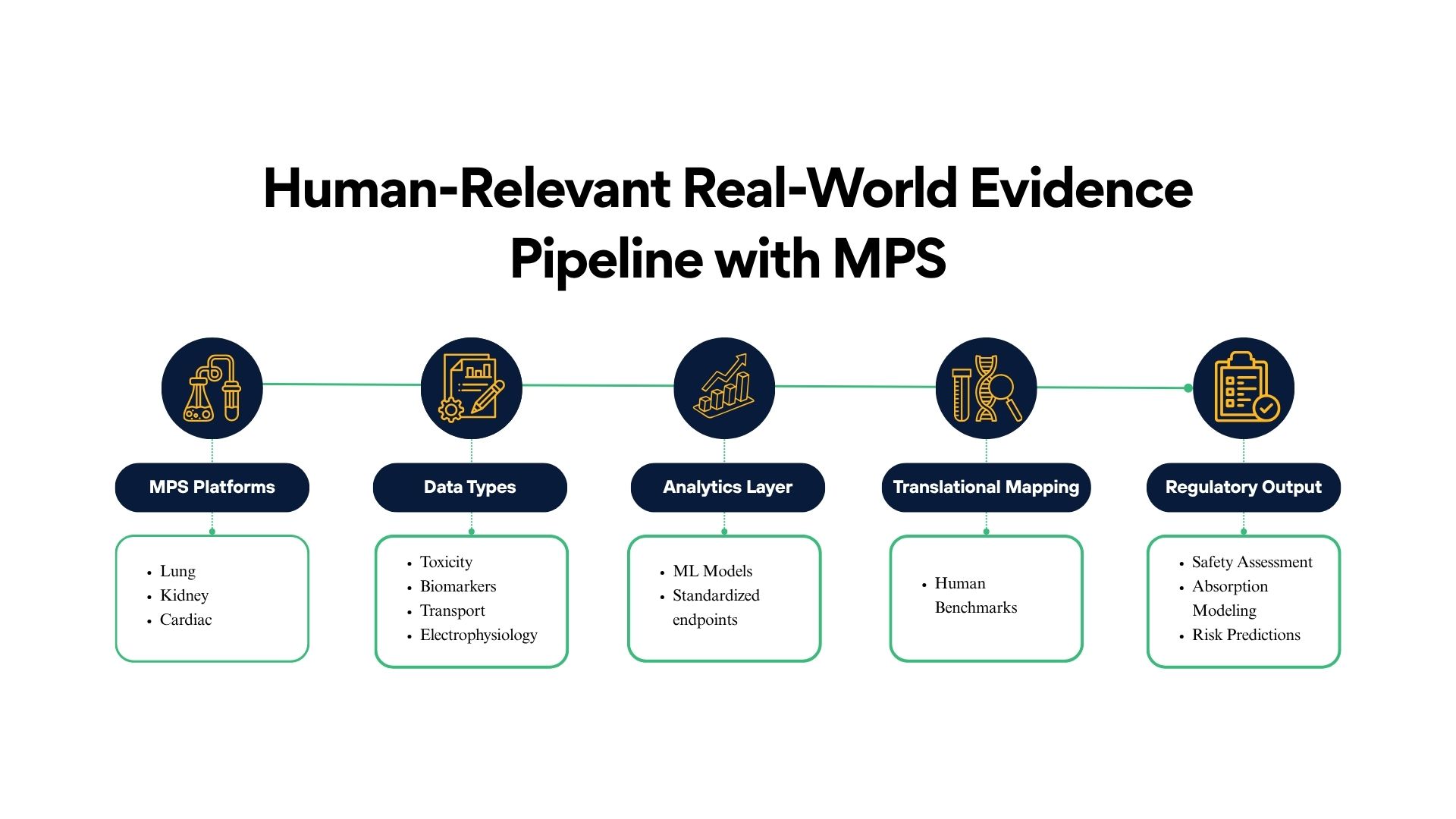
Cognizance scientific teams helped FDA advance the regulatory use of MPS by developing and validating several high-fidelity organ systems and analytic frameworks.
1. Lung Microphysiological Systems for Drug Absorption & Safety
Regulatory impact: Supports OINDP (Orally Inhaled and Nasal Drug Products) evaluations for absorption, safety, and local toxicity.
2. Kidney MPS for Toxicity Biomarker Validation
Regulatory impact: Provides stronger human-relevant data for drug-induced kidney injury assessments.
3. Cardiac Safety NAMs & NAM-MPS Integration
Regulatory impact: Supports CDER’s movement toward in vitro cardiac safety platforms beyond the hERG assay.
4. Machine Learning Approaches to Standardize MPS Interpretation
Cognizance’s scientific teams contributed to best practices for:
Regulatory impact: Establishes transparent, reproducible data pipelines compatible with regulatory workflows.
5. Frameworks for Regulatory Adoption
Contributions include:
Regulatory impact: Aligns MPS development with FDA expectations for reproducibility and translational performance.
Cognizance’s work helped advance MPS as credible sources of real-world evidence for regulatory science.
✔ Demonstrated human-relevant mechanistic insights – Lung and kidney MPS accurately reproduced transport, toxicity, and permeability phenomena observed in humans.
✔ Validated translational biomarkers – Kidney and lung injury biomarkers showed predictive alignment with known human responses.
✔ Increased reproducibility and standardization – Harmonized workflows and ML frameworks reduced variability across labs.
✔ Enabled FDA reviewers to use MPS data – Submissions now include MPS-derived data for absorption, toxicity, and mechanistic interpretation.
✔ Enhanced drug safety predictions – NAM-based MPS systems supported early hazard identification, reducing late-stage failures and unnecessary animal use.
These contributions push MPS forward as part of the next generation of regulatory science tools.